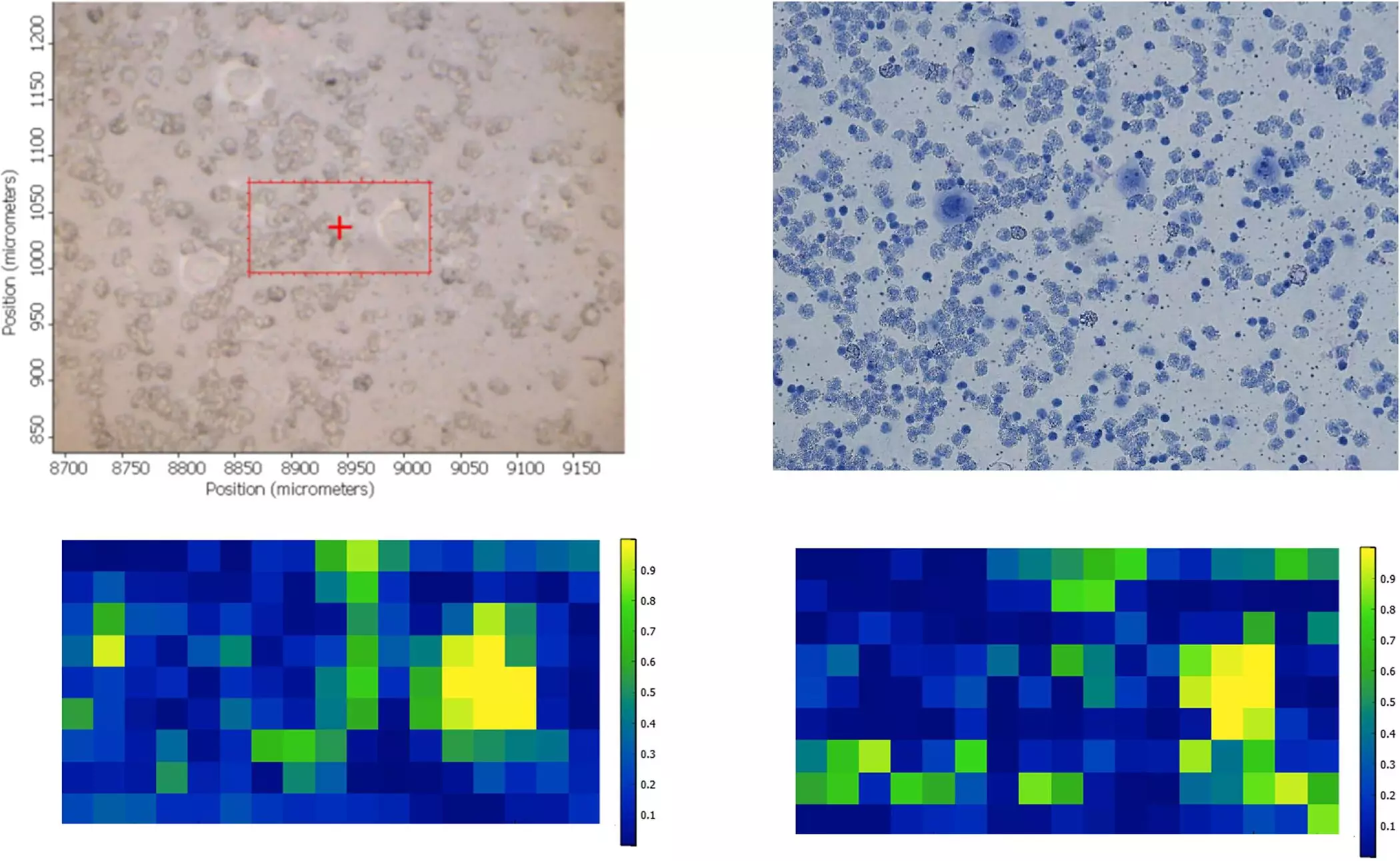
In a groundbreaking study conducted by a team of researchers led by Professor Josep Suñé-Suso from Keele University, a new method for identifying single cancer cells in blood samples has been discovered. This groundbreaking discovery has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment by allowing for more personalized and targeted therapies for patients.
The team of academics utilized a technique known as Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) microspectroscopy to separate cells based on their biochemical composition using an infrared light. By combining this method with a machine learning algorithm, the researchers were able to successfully identify a single lung cancer cell in a sample of blood, as published in the journal PLOS One.
The emergence of personalized medicine has significantly improved the treatment of cancer patients by tailoring therapies to individual needs and specific cancer types. By identifying individual tumor cells circulating in the blood, patients can be more effectively monitored during various stages of cancer treatment, from initial screening to follow-up.
The researchers have received approval to expand their study to include blood samples from patients with various types of cancer, not just limited to lung cancer. This aims to determine if the FTIR microspectroscopy technique can be replicated successfully across different cancer types. The potential implications of this research are promising and could set new standards for cancer treatment at all stages.
Professor Kamaraj Karunanithi from the University Hospitals of North Midlands NHS Trust expressed excitement about the research targeting the early detection of cancer cells in the bloodstream. Early detection of cancer spread is crucial for improving patient care, and this new method could potentially change the landscape of cancer treatment by enabling quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
The identification of single cancer cells in blood samples marks a significant advancement in the field of oncology. This groundbreaking research opens up new possibilities for more effective cancer treatment and management. As the study continues to expand, the potential for personalized medicine in cancer care continues to grow, offering hope for improved outcomes for patients in the future.